HW 18 postponed to
Monday March 8, 1999
Next test starts Friday March 5, 1999. It will cover Chapters
29-30.7. There are 24 MChoice and 1 HW style problems.
Wed March 10 is a $3.25 late day.
Extra credit for Assignment 21 due P7, not P9
Extra credit needs to be turned in with the assignment where it is due.
The graders are posting the solutions after that.
Review-Chapter 29
-
The force on a charged particle moving in a magnetic field.
-
Alternate right hand rule:
-
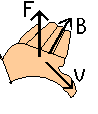 To find the direction
of the force on a moving + charge, point your thumb in the direction of
,v, point your fingers in the direction of B, and
the force is out of the palm of your hand. NOTE: when solving problems
using the right hand rule: north is not up, down is not south, and for
most of us, if we are holding our pencil we are not using our right hand.
To find the direction
of the force on a moving + charge, point your thumb in the direction of
,v, point your fingers in the direction of B, and
the force is out of the palm of your hand. NOTE: when solving problems
using the right hand rule: north is not up, down is not south, and for
most of us, if we are holding our pencil we are not using our right hand.
-
The magnitude of the force is:
-

-
The force on a current carrying wire is found
in a similar manner.

Examples: HWS II3,12,23,26
-
Torques and magnetic moments.
(the magnetic field created by the current points in the same direction
as the magnetic moment)

-
-
Here I is the total current in all the loops put together. That is, N turns
times the currect in each loops. I=iN

Magnetic moments want to line up with
the field.
-
Examples: HWS II 5,17
-
Hall effect-Current moving through a magnetic
field will create a potential difference across the wire.
Chapter
30
-
Biot-Savart law- > use to find B for configurations
of wires where there is little or no symmetry.
-
i.e. short pieces of wire, weird shapes etc.
-
Examples HWS 2,9,30
-
Ampere's law -> use to find B when there is
a lot of symmetry.
-
i.e. infinite pieces of
wire, long solinoids, toroids, etc.
-

-
(Sometimes I must be found from current density.)
-
Please do some of these examples: HWS 6,16,19,27 and Chapter 30:p31
(page 896)
-
Magnetic flux and Gauss's Law for Magnetism.
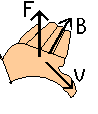 To find the direction
of the force on a moving + charge, point your thumb in the direction of
,v, point your fingers in the direction of B, and
the force is out of the palm of your hand. NOTE: when solving problems
using the right hand rule: north is not up, down is not south, and for
most of us, if we are holding our pencil we are not using our right hand.
To find the direction
of the force on a moving + charge, point your thumb in the direction of
,v, point your fingers in the direction of B, and
the force is out of the palm of your hand. NOTE: when solving problems
using the right hand rule: north is not up, down is not south, and for
most of us, if we are holding our pencil we are not using our right hand.